Last month, a customer who has been cooperating with our company for more than 3 years asked me what injection molding is. I was surprised hear this question. Prior to that, he had been purchasing injection molding parts from our company for 3 years.
I think there are probably a lot of people who don’t know what about injection molding, Today I will take you to understand the process of injection molding, material, surface treatment, application scenarios by this articles.
What is injection molding ?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves the use of a machine to inject plastic material into a mold. The mold is then heated until the plastic solidifies, resulting in the creation of a finished product.
Plastic injection molding is often used to create products such as bottles, cups, toys and automotive parts . In this article, we will discuss the definition of injection molding, the process involved, the different types of materials that can be used, and the surface finish that can be achieved. We will also provide some tips on how to choose a factory when outsourcing your injection molding needs.
What is injection molding process?
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that can be used to create products from a wide variety of materials.
The injection molding process is fairly straightforward. First, a mold is created in the shape of the desired product. Next, molten plastic is injected into the mold using a high-pressure machine. The mold is then cooled until the plastic solidifies. Once solidified, the product can be removed from the mold and will be ready for use.
What is injection molding machine?
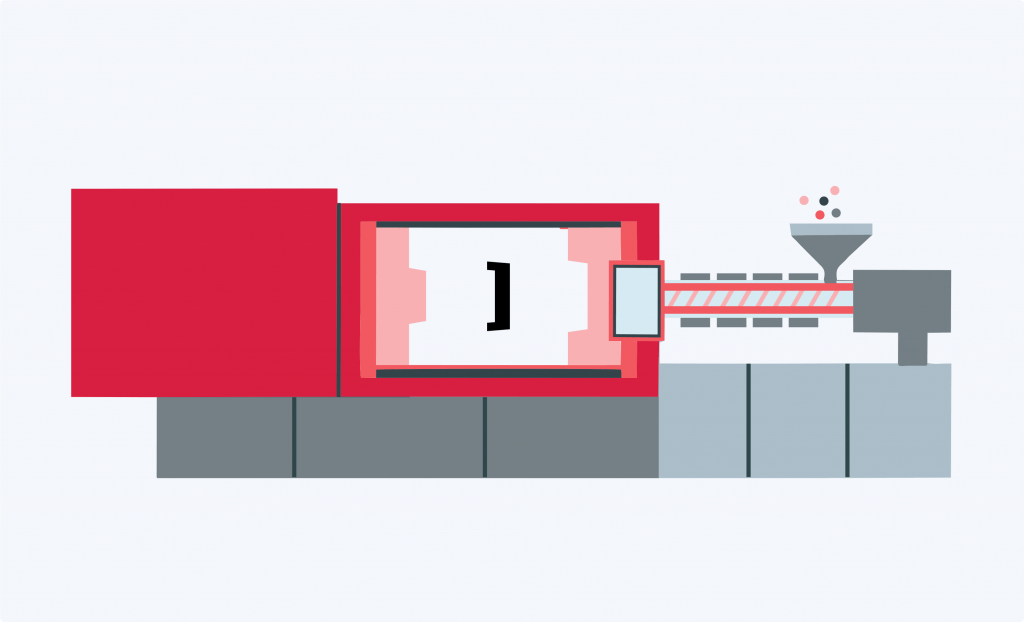
The injection molding machine is the key component in the plastic injection moulding process. It consists of a barrel, where the molten plastic is stored, and a plunger, which injects the plastic materials into the mold. The injection molding machines also includes a heating element, which melts the plastic prior to injection, injection unit, injection mold cavity, speed and pressure control system and a cooling system, which cools the plastic after it has been injected. the key factors affecting the quality of parts are injection speed and injection pressure.
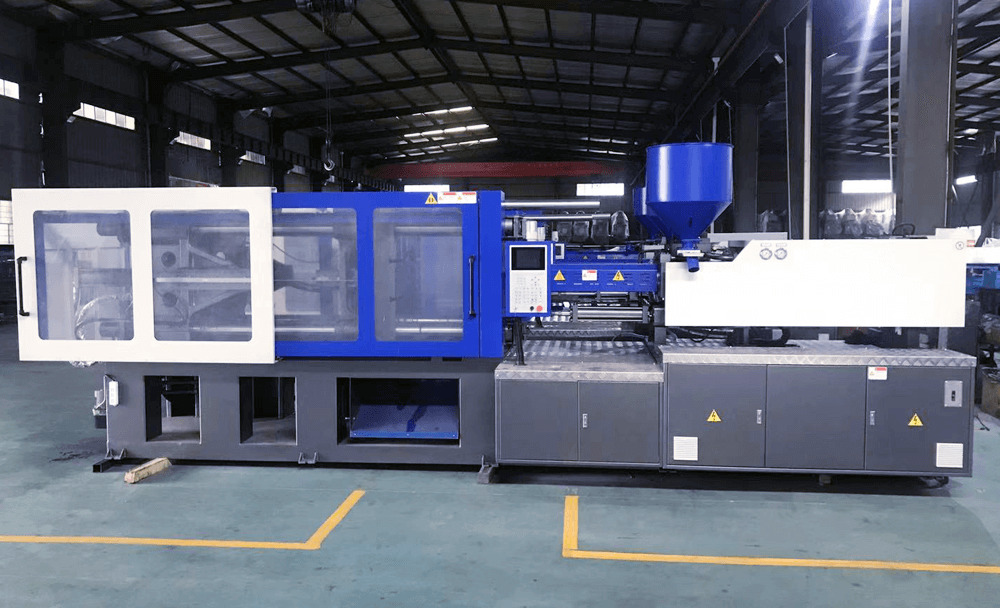

How to make injection molding mould?
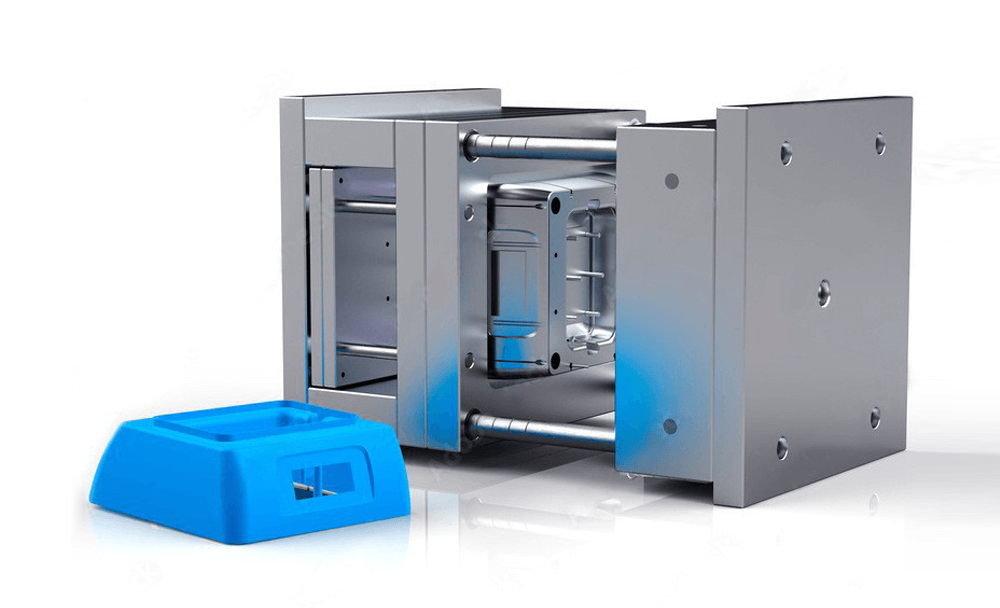
Injection molds are typically made from steel or aluminum. The metal mold is created by first machining a negative of the desired product shape into the metal. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as CNC machining or EDM (electrical discharge machining). Once the negative has been created, it is then used to create a positive mold. This is typically done by pouring molten metal into the negative and allowing it to cool. Once cooled, the positive mold can be used to create products using the injection moulding process.
The type of injection mould including and single cavity mould and multiple cavity moulds. the multiple cavity mould can be used in overmolding and insert molding.
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
The types of plastic injection molding
1.Distinguish by material
There are two main types of plastic injection moulding: thermosetting and thermoplastic.
Thermosetting plastic is a type of plastic that becomes hard and rigid when heated. This type of plastic is often used in the creation of products such as auto parts, electrical components, and cooking utensils.
2.Distinguish by product process
There are two kinds of injection molding commonly used:Overmolding and Insert molding.
- Over molding is a manufacturing processes where one material is molded over another. This is often used when a product needs to have two different colors or two different materials. It can be found in the production of toys, handles, and electronic housings.
- Insert molding is a process where a pre-formed insert is placed into a mold before the injection process begins. This type of molding is often used when creating products that need to be strong and durable, such as car parts or medical apparatus. It can be found in the production of car parts, medical apparatus, and electrical components.
Which plastic materials can be used in Injection Moulding?

The materials used for plastic injection molding generally depend on the purpose of the product, Commonly used injection molding materials are ABS, PC, LCP, Nylon,PE, PET, PEI, LDPE, HDPE, and PP. These materials can be found in products ranging from medical apparatus to electronic components.
The following is the basic introduction of commonly used injection materials
ABS is a thermoplastic material that is used in many injection moulding products. It is known for its impact resistance, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. ABS is often used in the creation of products such as toys, automotive parts, and electronic housings.
- PC (Polycarbonate)
Polycarbonate is a high molecular weight polymer. It is known for its high strength, rigidity, and transparency. PC is often used in the creation of products such as medical
instrument, optical lenses, and electronic components.
- LCP(Liquid Crystal Polymer)
Liquid Crystal Polymer is a new type of polymer material, It is known for its high strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. LCP is often used in the creation of products such as medical
instrument, electrical components, and automotive parts.
- Nylon
There are many types of nylon, and different types have different characteristics.Common types are Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Nylon 11. Among all nylon grades, nylon 6 has the lowest modulus. It is known for its high strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance. Nylon is often used in the creation of products such as ropes, nets, and brushes.
PE ( Polyethylene )
The full name is Polyethylene, It is known for its low density, high strength, and low moisture absorption. PE is often used in the creation of products such as pipes, fittings, and bottles.
PET ( Polyethylene terephthalate )
Polyethylene terephthalate is a highly crystalline polymer with a smooth and shiny surface.. It is known for its high strength, rigidity, and transparency. PET is often used in the creation of products such as food containers, water bottles, and medical devices.
PEI ( Polyetherimide )
Polyetherimide is an super engineering plastic. It is known for its high strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. PEI is often used in the creation of products such as electrical components, medical devices, and automotive parts.
LDPE (Low-density polyethylene)
Low-density polyethylene is milky white, odorless, odorless, non-toxic, and waxy particles with a matt surface. It is known for its low density, high strength, and flexibility. LDPE is often used in the creation of products such as bags, tubing, and packaging film.
HDPE ( High-density polyethylene )
High-density polyethylene is a white powder or granular product. It is known for its high strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance. HDPE is often used in the creation of products such as pipes, tanks, and containers.
PP ( Polypropylene )
Polypropylene is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, translucent solid substance. It is known for its high strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance. PP is often used in the creation of products such as pipes, fittings, and containers.
The surface finish of plastic injection molding parts
The surface finish of manufacturing plastic parts can vary depending on the type of material used and the desired look of the finished product. There are surface finish grades that range from rough to smooth. A higher grade surface finish will have a smoother appearance and may be more resistant to wear and tear.
The most common type of finish is a glossy finish. This type of finish is created by using a high-pressure machine to inject the plastic into the mold.
A matte finish can also be achieved by using a lower-pressure machine. This type of finish is often used for products that will be handled frequently, such as cups or toys.
In addition to surface finish, the factors that affect the appearance of injection parts are the surface coating of injection plastic parts, So which are the process of coating for injection molding parts?
The process of coating for injection moulding parts can be either physical or chemical. Physical coatings include painting, powder coating, and plating. Chemical coatings include anodizing and electroplating.
What coating process are the injection molded parts?
In order to protect the surface of injection mould parts from wear and tear, it is often necessary to coat the part. The most common type of coating is a powder coating. This type of coating is created by spraying a dry powder onto the surface of the part. The powder adheres to the surface and creates a protective layer.
Other types of coatings include painting, plating, and heat staking. Each type of coating has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The following is the basic introduction of commonly used injection materials
Painting
Painting is a common type of coating for plastic injection moulding parts. It is a relatively simple process and can be done quickly. Painting provides a durable finish that is resistant to wear and tear.
Powder Coating
Powder coating is another common type of coating for injection moulding parts. Powder coating is created by spraying a dry powder onto the surface of the part. The powder adheres to the surface and creates a protective layer. Powder coating is more durable than painting and provides a higher level of protection against wear and tear.
Heat Staking
Heat staking is a process that is used to join two pieces of plastic together. Heat staking uses heat to melt the plastic and create a strong bond between the two pieces.
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is a process that uses a laser to etch a design into the surface of the part. Laser engraving is permanent and cannot be removed.
Plating
Plating is a process that uses a metal to coat the surface of the part. Plating provides a durable finish that is resistant to wear and tear.
The standard tolerances for injection molded parts
Most injection molding factory have two kind of manufacturing tolerances. One is standard tolerance, the other is high precision tolerance. Because of the characteristics of different materials, the tolerance standards of finished moulding parts are different.
To improve the reading experience, the mobile only display standard tolerances, while high precision tolerances can be viewed on the PC
Dimensional Tolerances +/- mm
| Standard Tolerance | High Precision Tolerance | ||||
| Dimensions | 1~20 (+/-mm) | 20~100 (+/-mm) | 101~160 (+/-mm) | 1~20 (+/-mm) | 20~100 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 | 0.050 | 0.100 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 | 0.050 | 0.100 |
| GPS | 0.075 | 0.150 | 0.305 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| HDPE | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.325 | 0.075 | 0.110 |
| LDPE | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 | 0.075 | 0.110 |
| PPO/PPE | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 | 0.075 | 0.110 |
| PA | 0.075 | 0.160 | 0.310 | 0.030 | 0.130 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 | 0.030 | 0.100 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 | 0.030 | 0.100 |
| PC | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 | 0.030 | 0.100 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.200 | 0.030 | 0.080 |
| PMMA | 0.075 | 0.120 | 0.250 | 0.050 | 0.070 |
| POM | 0.075 | 0.160 | 0.310 | 0.030 | 0.130 |
| PP | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 | 0.075 | 0.110 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 | 0.075 | 0.110 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 | 0.030 | 0.100 |
| Standard Tolerance | |||
| Dimensions | 1~20 (+/-mm) | 20~100 (+/-mm) | 101~160 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 |
| GPS | 0.075 | 0.150 | 0.305 |
| HDPE | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.325 |
| LDPE | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 |
| PPO/PPE | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.325 |
| PA | 0.075 | 0.160 | 0.310 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 |
| PC | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.200 |
| PMMA | 0.075 | 0.120 | 0.250 |
| POM | 0.075 | 0.160 | 0.310 |
| PP | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.125 | 0.170 | 0.375 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.060 | 0.120 | 0.240 |
Straightness/Flatness Tolerance +/- mm
| Standard Tolerance | High Precision Tolerance | |||
| Dimensions | 0~100 (+/-mm) | 101~160 (+/-mm) | 1~20 (+/-mm) | 20~100 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.380 | 0.800 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.380 | 0.800 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| Acetal | 0.300 | 0.500 | 0.150 | 0.250 |
| GPS | 0.250 | 0.380 | 0.180 | 0.250 |
| PPO/PPE | 0.380 | 0.800 | 0.250 | 0.250 |
| PA | 0.300 | 0.500 | 0.150 | 0.250 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PC | 0.150 | 0.200 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.130 | 0.180 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PE | 0.85 | 1.500 | 0.500 | 0.850 |
| PP | 0.85 | 1.500 | 0.500 | 0.850 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.85 | 1.500 | 0.500 | 0.850 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| Standard Tolerance | ||
| Dimensions | 0~100 (+/-mm) | 101~160 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.380 | 0.800 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.380 | 0.800 |
| Acetal | 0.300 | 0.500 |
| GPS | 0.250 | 0.380 |
| PPO/PPE | 0.380 | 0.800 |
| PA | 0.300 | 0.500 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 |
| PC | 0.150 | 0.200 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.130 | 0.180 |
| PE | 0.85 | 1.500 |
| PP | 0.85 | 1.500 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.85 | 1.500 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.150 | 0.200 |
Bore Diameter Tolerances +/- mm
| Standard Tolerance | High Precision Tolerance | |||||
| Dimensions | 1~6 (+/-mm) | 6.1~14 (+/-mm) | > 14 (+/-mm) | 1~6 (+/-mm) | 6.1~14 (+/-mm) | > 14 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| GPS | 0.090 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| HDPE | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| LDPE | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PA | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| PC 20% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| PMMA | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.200 | 0.030 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PMMA | 0.075 | 0.120 | 0.250 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PC | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| PP | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.080 |
| Standard Tolerance | |||
| Dimensions | 1~6 (+/-mm) | 6.1~14 (+/-mm) | > 14 (+/-mm) |
| ABS | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| ABS/PC mix | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| GPS | 0.090 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| HDPE | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 |
| LDPE | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 |
| PA | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| PA 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PBT 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PC 20% GF | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PMMA | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
| PC 20% Glass | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.200 |
| PMMA | 0.075 | 0.120 | 0.250 |
| PC | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.100 |
| PP | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 |
| PP 20% Talc | 0.100 | 0.120 | 0.150 |
| PPS 30% GF | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.130 |
The application of injection molding
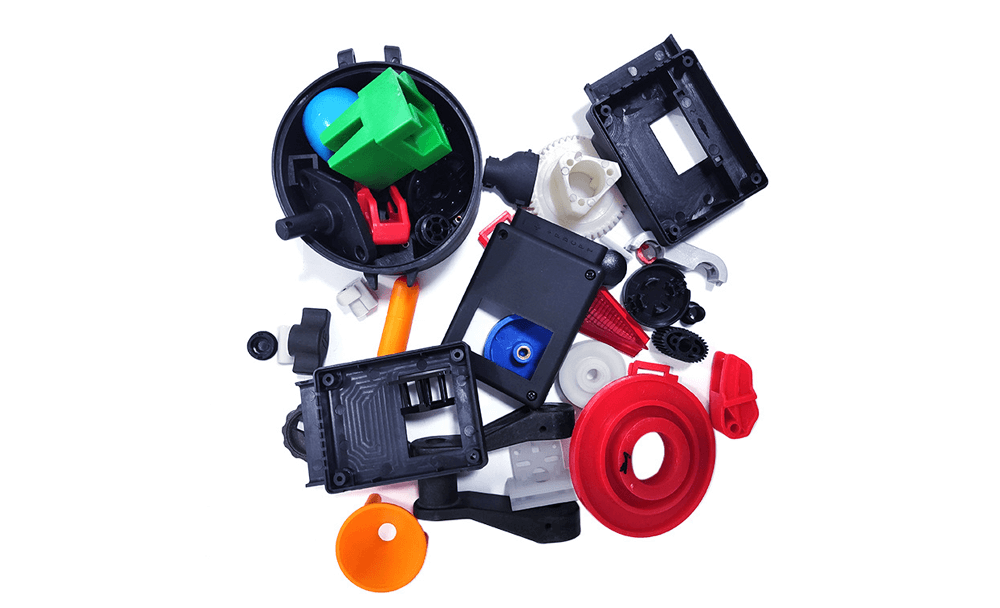

Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that can be used to create products from a wide variety of materials. The most common applications for injection moulding parts are in the plastic containers, toys, plumbing fittings, electrical components, telephones receivers, automotive parts, electrical, and medical industries. Injection molding can also be used to create consumer products, such as toys and toothbrushes.
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
3D printing VS Injection molding
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, it is used to create three-dimensional objects by successively depositing material in layers. The processes have been developed in which materials are joined or solidified under computer control to create products from three-dimensional (CAD) data, usually layer by layer.
The main difference between the two is that injection molding parts are typically mass-produced, while three-dimensional printed parts are typically produced one at a time.
Injection molding is typically used for mass products that require a large quantity to be produced, such as bottles or cups. Three-dimensional printing is typically used for prototype development or for low-volume production runs.
CNC Machining VS Injection molding
CNC machining is a process that removes material from a workpiece to create a desired shape or geometry. The process is controlled by a computer program that tells the machine what to do. Injection moulding is a machining process that injects molten plastic into a mold to create parts.
The main difference between the two processes is that CNC machining is a subtractive production process and plastic injection moulding is an additive production process.
Injection moulding is typically used for products that require a large quantity to be produced, such as bottles or cups. CNC machining is typically used for prototype development or for low-volume production runs.
CNC machining is also typically more accurate than plastic injection moulding.
The advantages of injection molding
Injection moulding is a versatile production process that has many benefits. Injection moulding parts are strong, lightweight, and can be created from a wide variety of materials. Injection moulding is also a fast and efficient production process that can be used to create large quantities of parts.
Injection moulding has a number of advantages over other manufacturing processes, including:
-It is a fast and efficient way to high volume production parts.
-It is relatively easy to automate, which results in lower labor costs.
-Injection moulding parts have consistent dimensions and can be very precise.
-The surface finish of injection moulding parts is typically very smooth.
-Injection molding can be used to produce parts from a variety of different materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
-No waste material is produced during injection molding.
The disadvantages of injection molding
There are also some disadvantages to using plastic injection molding, including:
-The initial investment in equipment and tooling can be high.
-There is a limited range of shapes and sizes that can be injection moulded.
-Injection molding is not well suited for the production of small quantities of parts.
-The lead time for injection molding parts can be long, due to the need to design and build the mold.
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
What are the production costs of injection molding parts?
The injection moulding costs of injection molding parts are affected by a number of factors, such as the type of material used, the complexity of the part, the size of the part, and the quantity of parts produced.
In order to reduce the production costs of plastic injection molding parts, it is important to choose a reputable and experienced injection molding factory. A good factory will be able to provide a high quality product at a competitive price.
What is the production cycle of the injection molding project?
The production cycle of an injection molding project typically includes the following steps:
-Design and development of the mold.
-Purchase of plastic raw material
-Injection molding of the parts.
-Surface treatment of injection parts.
-Assembly of the parts.
-Testing
– Mass Production
Every step needs to go through strict quality inspection.
The common problems in the injection molding industry
The most common problems in the plastic injection molding industry are:
-Poor quality control.
-Inefficient production processes.
-Lack of skilled labor.
-High production costs.
These problems can be addressed by working with a reputable and experienced injection molding factory. A good factory will have strict quality control procedures in place and will use efficient production processes to minimize costs. They will also have a team of skilled workers who can produce high quality parts.
Things to consider when choosing an injection molding factory
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing an injection molding factory, including the location of the factory, the size of the factory, and the experience of the staff. The location of the factory is important because it can affect the cost of transportation and shipping.
The size of the factory is also important because it can affect the economies of scale. The experience of the staff is important because it can affect the quality of the parts produced. When choosing an injection molding factory, it is important to consider all of these factors in order to get the best value for your money.
When choosing an plastic injection molding factory, it is important to consider the following factors:
-The experience of the factory: The more experience a factory has, the better they will be at manufacturing high quality parts.
-The size of the factory: A larger factory will be able to produce parts more quickly and at a lower cost.
-The location of the factory: A factory that is located in a country with a low labor cost will be able to produce parts at a lower cost.
-The type of equipment used by the factory: The type of equipment used by the factory will affect the quality of the parts produced.
-The reputation of the factory: A reputable factory will be able to provide a high quality product at a competitive price.
There are a number of reputable and experienced injection molding factories located in China that can provide high quality parts at a competitive price.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plastic injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that can be used to create products from a wide variety of materials. The most common applications for injection molding parts are in the plastic containers, toys, plumbing fittings, electrical components, telephones receivers, automotive parts, electrical, and medical industries. In order to reduce the production costs of injection mould parts, it is important to choose a reputable and experienced injection molding factory. A good factory will be able to provide a high quality product at a competitive price.
We hope this article has provided you with a basic understanding of injection molding and the factors you should consider when choosing an injection molding factory. If you are in need of high-quality injection parts, please contact us today. We would be happy to discuss your project with you and provide a quote. Thank you for reading!
Try Made by Aria Now
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
Categories
Share On
Recent Post